Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wakai, Satoshi*; Hirano, Shinichi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Okamoto, Akihiro*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.491 - 496, 2021/12
After Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, various corrosion mitigating activities have been treated, and severe corrosion incident have never taken placed. On the other hand, the facilities were exposed sea water, and some of them have continuously exposed to ground water. The exposure of metal materials to environmental water has a risk of microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC). In this paper, we summarize the latest knowledge of MIC and the task of MIC in the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
Saga, Ryo*; Matsuya, Yusuke; Takahashi, Rei*; Hasegawa, Kazuki*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Hosokawa, Yoichiro*
Journal of Radiation Research, 60(3), p.298 - 307, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:82.31(Biology)In radiotherapy, it is recognized that cancer stem cells (CSCs) in tumor tissue shows radio-resistance. However, the relationship between content percentage of the CSCs and dose-response curve on cell survival remain unclear. In this study, we developed a stochastic model considering progeny cells and stem cells, and investigated the impact of stem cells on radio-sensitivity. From the flow-cytometric analysis (cell experiments), the content percentage of stem cells was 3.2% or less which agreed well with the model estimation from the cell survival curve. Based on the verification, it is suggested that cell survival in high-dose range is largely affected by the CSCs. In addition, regarding the sub-population of stem cells, the present model well reproduces the dose response on lethal lesions to DNA comparing with the conventional LQ model. This outcome indicates that the stem cells must be considered for describing the dose-response curve in wide dose range.
Kado, Masataka; Kishimoto, Maki; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Yasuda, Keiko*; Aoyama, Masato*; Tone, Shigenobu*; Shinohara, Kunio*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1696, p.020019_1 - 020019_4, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:85.37(Microscopy)Soft X-ray microscope is a very powerful tool to observe cellular organelles of living biological cells and many works have demonstrated imaging of inner structures of the cells. However the inner structures are very complicated and it is difficult to identify the organelles obtained with the soft X-ray microscopes. We have proposed a hybrid imaging method with a soft X-ray microscope and a fluorescence microscope that is to observe the same biological cells with the both microscopes at the same time. Using the information of the cellular organelles obtained with the fluorescence microscope, inner structures obtained with the soft X-ray microscope are accurately identified. We have observed living biological cells by the hybrid imaging method. Since the soft X-ray microscope has higher spatial resolution than that of the fluorescence microscope, fine structures of the cellular organelles in the living biological cells were discussed.
Hattori, Yuya; Yokoya, Akinari; Watanabe, Ritsuko
BMC Systems Biology (Internet), 9, p.90_1 - 90_22, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:66.16(Mathematical & Computational Biology)The radiation-induced bystander effect is a biological response observed in non-irradiated cells surrounding an irradiated cell, which is known to be caused by two intercellular signaling pathways. However, the behavior of the signals is largely unknown. To investigate the role of these signaling pathways, we developed a mathematical model to describe the cellular response to direct irradiation and the bystander effect, with a particular focus on cell-cycle modification. The analysis of model dynamics revealed that bystander effect on cell cycle modification was different between low-dose irradiation and high-dose irradiation. We demonstrated that signaling through both pathways induced cell cycle modification via the bystander effect. By simulating various special and temporal conditions of irradiation and cell characteristics, our model will be a powerful tool for the analysis of the bystander effect.
Ouchi, Noriyuki
Evolution of Ionizing Radiation Research, p.41 - 62, 2015/09
Quantitative approach in radiation biology based on the clonogenic method and obtained cell survival curves as a dose-response relationship, are introduced. Generally, cell survival curves seem to have a universality on its function, i.e. functional form of survival curve seems to be unchanged under various conditions including different species. Various factors affecting the radiosensitivity have been introduced to find macroscopic nature of living organisms. Many mathematical models describing cell survival curves have been presented, however, functional form of cell survival curves derived from, based on biological mechanism does not yet exist. Finally, the possibility that the structural change of chromosome affects the repair process is discussed.
Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 73, 2015/03
Using a collimating heavy-ion microbeam system, we have explored various effects of heavy-ion hit on biological materials. However, there are limitations of the collimating system in the size of the microbeam spot and in the irradiation speed that cannot be overcome in principle. Thus, we started the development of a focusing microbeam system for target-irradiating individual cells more precisely. In this year, we established the protocol for irradiating "actual" cell sample with scanned beam. In the experiment, the HeLa cells were inoculated on a CR-39 film, then place on the sample stage. The microscopic image of cells was analyzed, and the cells were irradiated with scanned neon microbeam. After irradiation, we found the correspondence of the distribution pattern of the ion hit positions and the  -H2AX foci on cell nuclei, indicating rapid and accurate irradiation of individual cells with the focusing heavy-ion microbeam.
-H2AX foci on cell nuclei, indicating rapid and accurate irradiation of individual cells with the focusing heavy-ion microbeam.
Wada, Seiichi*; Ando, Tatsuhiko*; Watanabe, Aya*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Natsuhori, Masahiro*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 79, 2015/03
So far, we clarified that X-ray irradiation induced cell killing by bystander effect mediated-secreted factor. This phenomenon was related with sphingomyelinase (SMase). In this study we analyzed mechanism of secreted SMase from irradiated cells after irradiation. SMase was detected in the culture medium after irradiation by SDS-PAGE. Then, SMase was detected in the exosome of culture medium, but not out of exosome after irradiation. This result indicates that SMase was secreted as exosome from the irradiated cells.
 C and
C and  He
HeAkeo, Kiyoshi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Akeo, Yoko*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 80, 2015/03
It is known that superoxide dismutases (SOD) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the dismutation of superoxide into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. Ionizing radiation is known to induce oxidative stress through generation of reactive oxygen species resulting in imbalance of the pro-oxidant and antioxidant in the cells, which is suggested to culminate in cell death. Therefore, we measured the activity of SOD in human RE cells exposed to the He- and C-ion beam. The cells collected at 0, 4, 8, and 24 hr after irradiation were extracted by adding the SOD assay buffer to the pellets, and lysed by several cycles of freezing and thawing. The activity of SOD was measured using a modification of the luminol assay. SOD activity decreased according to duration time after irradiation of He-ion, however, in case of C-ion, it increased at 24 hr after irradiation. The result suggested that that there were the differences of the effects by irradiation on SOD activity between He- and C-ion.
Yokoya, Akinari; Kaminaga, Kiichi
Hoshasen Seibutsu Kenkyu, 49(4), p.418 - 431, 2014/12
no abstracts in English
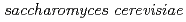
Onuki, Toshihiko; Ozaki, Takuo; Yoshida, Takahiro*; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Wakai, Eiichi; Francis, A. J.; Iefuji, Haruyuki*
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(22), p.5307 - 5316, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:68.15(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
Kinase, Sakae; Yokoya, Ritsuko; Saito, Kimiaki
KEK Proceedings 2005-10 (CD-ROM), p.33 - 38, 2005/11
The aim of the present work has been the development of logical dosimetry for human alimentary tract. In this work, a stomach simple model with stem cells has been developed. Also, specific absorbed fractions for photon and electron to the stomach model have been evaluated in the energy range 10 keV-4MeV using Monte Calro simulation. Consequently, it was found that photon SAFs to the stem cell in the stomach are more than those to the stomach wall. Electron SAFs to the stem cell in the stomach were also found to be less than that used in the radiological protection. It is concluded that the Monte Carlo simulation is very useful in the development of logical dosimetry for the stomach and that the determination of target tissue in the stomach is very important for the SAF evaluation.
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Furusawa, Yoshiya*
KEK Proceedings 2005-5, p.6 - 8, 2005/10
no abstracts in English
 rays
raysYokota, Yuichiro; Shikazono, Naoya; Tanaka, Atsushi; Hase, Yoshihiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Inoue, Masayoshi*
Radiation Research, 163(5), p.520 - 525, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:50.54(Biology)Higher plants are generally more tolerant to ionizing radiation than mammals. To explore the radiation tolerance of higher plants, the amount of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) induced by  -rays was investigated in tobacco BY-2 cells and compared with that investigated in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO)-K1 cells as a reference. The resulting DNA fragments were separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and stained with SYBR Green I. Initial DSB yield was then quantified from the fraction of DNA fragments shorter than 1.6 Mbp based on the assumption of random distribution of DSBs. The DSB yield in tobacco BY-2 cells (2.0
-rays was investigated in tobacco BY-2 cells and compared with that investigated in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO)-K1 cells as a reference. The resulting DNA fragments were separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and stained with SYBR Green I. Initial DSB yield was then quantified from the fraction of DNA fragments shorter than 1.6 Mbp based on the assumption of random distribution of DSBs. The DSB yield in tobacco BY-2 cells (2.0  0.1 DSBs Gbp
0.1 DSBs Gbp Gy
Gy ) was only one-third of that in CHO-K1 cells. Furthermore, the calculated number of DSBs per diploid cell irradiated with
) was only one-third of that in CHO-K1 cells. Furthermore, the calculated number of DSBs per diploid cell irradiated with  -rays of mean lethal dose was five times greater in tobacco BY-2 cells (263.2
-rays of mean lethal dose was five times greater in tobacco BY-2 cells (263.2  13.2) than in CHO-K1 cells. These results suggest that the radiation tolerance of tobacco BY-2 cells appears to be due to not only a lower induction of DNA damage but also a more efficient repair of the induced DNA damage.
13.2) than in CHO-K1 cells. These results suggest that the radiation tolerance of tobacco BY-2 cells appears to be due to not only a lower induction of DNA damage but also a more efficient repair of the induced DNA damage.
Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Radiation Research, 163(2), p.241 - 246, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:64.71(Biology)As the first step for the analysis of the biological effect of heavy charged-particle radiation, we established a method for the irradiation of individual cells with a heavy ion microbeam apparatus at JAERI-Takasaki. CHO-K1 cells attached on the thin film of ion track detector, CR-39, were automatically detected under fluorescent microscope, and irradiated individually with  Ar
Ar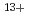 ion (11.5 MeV/u, LET=1260 keV/
ion (11.5 MeV/u, LET=1260 keV/ m) microbeam. Without killing the irradiated cells, trajectories of irradiated ions were visualized as etch-pits by treatment of CR-39 with alkaline-ethanol solution at 37
m) microbeam. Without killing the irradiated cells, trajectories of irradiated ions were visualized as etch-pits by treatment of CR-39 with alkaline-ethanol solution at 37 C. The exact positions of ion hits were determined by overlaying images of both cells and etch-pits. The cells that were irradiated with argon ions showed a reduced growth in post-irradiate observations. Moreover, a single hit of an argon ion to the cell nucleus resulted in strong growth inhibition. These results tell us that our truthful irradiation method now enables us to start a precise study of the cellular response of high-LET radiation effects on cells.
C. The exact positions of ion hits were determined by overlaying images of both cells and etch-pits. The cells that were irradiated with argon ions showed a reduced growth in post-irradiate observations. Moreover, a single hit of an argon ion to the cell nucleus resulted in strong growth inhibition. These results tell us that our truthful irradiation method now enables us to start a precise study of the cellular response of high-LET radiation effects on cells.
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Aoki, Mizuho*; Shao, C.*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshitaka*; Kakizaki, Takehiko; et al.
Uchu Seibutsu Kagaku, 18(4), p.235 - 240, 2004/12
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Sakashita, Tetsuya
Uchu Seibutsu Kagaku, 18(3), p.186 - 187, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Tomihiro; Hirao, Toshio; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 219-220, p.1010 - 1014, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:48.76(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Radiation Research, 161(1), p.90 - 91, 2004/01
A single cell irradiation system has been developed for targeting cells individually with a precise number of heavy ions to elucidate radiobiological effects of exactly one particle and to investigate the biological effects of low fluence irradiation with HZE particles. Using the heavy ion microbeam apparatus installed at JAERI-Takasaki, mammalian cells were irradiated in the atmosphere with a single or precise numbers of ions, 13.0 MeV/u 20Ne or 11.5 MeV/u 40Ar. The number of ions traversed the cells attached on the ion track detector CR-39 were counted with a plastic scintillator. Immediately after the irradiation, the position and the number of ion tracks traversed the cell was detected with etching of CR-39 from the opposite side of the cell with alkaline-ethanol solution at 37 C. The growths of the cells were observed individually up to 60 hours after irradiation.
C. The growths of the cells were observed individually up to 60 hours after irradiation.
Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Radiation Research, 161(1), p.111 - 112, 2004/01
Using the heavy ion microbeam apparatus, mammalian cells were irradiated in the atmosphere with a single or precise numbers of  Ar heavy ions (11.5 MeV/u) with a spatial resolution of a few microns. Positional data of the individual cells attached on the ion track detector CR-39 were obtained at the off-line microscope before irradiation, then the targeting and irradiation of the cells were performed semi-automatically at the on-line microscope of the microbeam apparatus according to the obtained data. Immediately after irradiation, the position and the number of ion tracks traversed the cell was detected with etching of CR-39 at 37
Ar heavy ions (11.5 MeV/u) with a spatial resolution of a few microns. Positional data of the individual cells attached on the ion track detector CR-39 were obtained at the off-line microscope before irradiation, then the targeting and irradiation of the cells were performed semi-automatically at the on-line microscope of the microbeam apparatus according to the obtained data. Immediately after irradiation, the position and the number of ion tracks traversed the cell was detected with etching of CR-39 at 37  C. The growths of the cells were observed individually up to 60 hours after irradiation. The continuous observation of the individual cell growth indicated that single Ar ion traversal of cell nucleolus resulted to complete growth inhibition of the irradiated cells.
C. The growths of the cells were observed individually up to 60 hours after irradiation. The continuous observation of the individual cell growth indicated that single Ar ion traversal of cell nucleolus resulted to complete growth inhibition of the irradiated cells.
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Watanabe, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210(1-4), p.308 - 311, 2003/09
A method for detecting the ion hit tracks on the mammalian cultured cells at the irradiation time was established. The cells were attached to the ion track detector CR-39 (100  m thick), then irradiated with 13.0 MeV/u 20Ne or 11.5 MeV/u 40Ar ion beams. Immediately after the irradiation, the cells were refilled with medium, then the CR-39 was etched from the opposite side of the cell with alkaline-ethanol solution at 37
m thick), then irradiated with 13.0 MeV/u 20Ne or 11.5 MeV/u 40Ar ion beams. Immediately after the irradiation, the cells were refilled with medium, then the CR-39 was etched from the opposite side of the cell with alkaline-ethanol solution at 37 C. With the 15 min etching treatment, we obtained the accurate information about the spatial distribution of irradiated ions without significant effect on the cell growth. The continuous observation of the individual cell growth indicated that the growth of ion hit cell was reduced compared with that of non-irradiated one.
C. With the 15 min etching treatment, we obtained the accurate information about the spatial distribution of irradiated ions without significant effect on the cell growth. The continuous observation of the individual cell growth indicated that the growth of ion hit cell was reduced compared with that of non-irradiated one.